| Chain Coupling No. | Chain No. | Bore Dia | Dimension | Inertia | Approx Weight | Casing | ||||||||
| Min | Max | L | I | S | d1 | d2 | C | ×10-3 | Dimension | Approx Weight | ||||
| A | B | |||||||||||||
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kgf·m2 | kg | mm | mm | kg | ||
| 3012 | 06B-2X12 | 12 | 16 | 64.8 | 29.8 | 5.2 | 25 | 45 | 10.2 | 0.233 | 0.4 | 69 | 63 | 0.3 |
| 4012 | 40-2X12 | 12 | 22 | 79.4 | 36.0 | 7.4 | 35 | 61 | 14.4 | 1.571 | 0.8 | 77 | 72 | 0.3 |
| 4014 | 40-2X14 | 12 | 28 | 79.4 | 36.0 | 7.4 | 43 | 69 | 14.4 | 1.924 | 1.1 | 84 | 75 | 0.4 |
| 4016 | 40-2X16 | 14 | 32 | 87.4 | 40.0 | 7.4 | 50 | 77 | 14.4 | 3.285 | 1.4 | 92 | 75 | 0.4 |
| 5014 | 50-2X14 | 16 | 35 | 99.7 | 45.0 | 9.7 | 53 | 86 | 18.1 | 6.571 | 2.2 | 101 | 85 | 0.5 |
| 5016 | 50-2X16 | 16 | 40 | 99.7 | 45.0 | 9.7 | 60 | 96 | 18.1 | 9.720 | 2.7 | 111 | 85 | 0.6 |
| 5018 | 50-2X18 | 16 | 45 | 99.7 | 45.0 | 9.7 | 70 | 106 | 18.1 | 15.420 | 3.8 | 122 | 85 | 0.8 |
| 6018 | 60-2X18 | 20 | 56 | 123.5 | 56.0 | 11.5 | 85 | 128 | 22.8 | 40.210 | 6.2 | 142 | 106 | 1.2 |
| 6571 | 60-2X20 | 20 | 60 | 123.5 | 56.0 | 11.5 | 98 | 140 | 22.8 | 62.870 | 7.8 | 158 | 105 | 1.6 |
| 6571 | 60-2X22 | 20 | 71 | 123.5 | 56.0 | 11.5 | 110 | 152 | 22.8 | 93.450 | 10.4 | 168 | 117 | 1.8 |
| 8018 | 80-2X18 | 20 | 80 | 141.2 | 63.0 | 15.2 | 110 | 170 | 29.3 | 142.030 | 12.7 | 190 | 129 | 2.5 |
| 8571 | 80-2X20 | 20 | 90 | 145.2 | 65.0 | 15.2 | 120 | 186 | 29.3 | 204.900 | 16.0 | 210 | 137 | 2.9 |
| 8571 | 80-2X22 | 20 | 100 | 157.2 | 71.0 | 15.2 | 140 | 202 | 29.3 | 341.170 | 20.2 | 226 | 137 | 3.6 |
| 1571 | 100-2X20 | 25 | 110 | 178.8 | 80.0 | 18.8 | 160 | 233 | 35.8 | 646.290 | 33.0 | 281 | 153 | 4.6 |
| 12018 | 120-2X18 | 35 | 125 | 202.7 | 90.0 | 22.7 | 170 | 256 | 45.4 | 1075.710 | 47.0 | 307 | 181 | 6.2 |
| 12571 | 120-2X22 | 35 | 140 | 222.7 | 100.0 | 22.7 | 210 | 304 | 45.4 | 2454.500 | 72.0 | 357 | 181 | 8.0 |
Chain Couplings
The chain coupling is composed of a duplex roller chain and a pair of coupling sprockets. The function of connection and detachment is done by the joint of the chain. It has the characteristic of being compact and powerful, excellent durability, safe and smart, simple installation and easy alignment. The chain coupling is suitable for a wide range of coupling applications.
Parameters of Chain Couplings
What Are Chain Couplings?
Chain couplings are mechanical devices for connecting 2 shafts. They consist of 2 rows of roller chains with sprockets that engage them. The shafts are then cranked to move the coupling. Chain couplings are available in a range of sizes and torque capacities.
Chain couplings are all steel and compact for space-constrained applications. They transmit high torques and offer positive power transmission. Unlike conventional couplings, chain couplings require less space and are easily installed and dismantled. They also provide a balanced unit operation, which is essential for high torques. Chain couplings are typically used in low-speed, high torque applications. They also offer a high degree of flexibility and allow for misalignment of up to 2 degrees between the shafts.
Advantages of a Chain Coupling
A chain coupling is a type of transmission system that uses a single common chain, meshing with 2 parallel sprockets to transfer power from 1 shaft to the other. A chain coupling comes in various varieties, including roller chain coupling, toothed chain coupling, and nylon chain coupling. The benefits of a chain coupling include its simplicity, reliability, and low installation accuracy. A chain coupling is a common option for shafting transmission applications, especially in low-speed, high-torque applications.
One of the most important advantages of chain couplings is their high-torque capability. Because they are made of 2 flanges linked by a duplex roller chain, they are ideal for high-torque applications. They can accommodate up to 2 degrees of misalignment, which makes them a common choice for applications that require high torque. Another advantage of chain couplings is their ease of installation and low-maintenance requirements.
Besides being easy to assemble, a chain coupling also keeps the 2 shafts perfectly aligned. It also minimizes shock and vibrations during power transmission. It should also have a low-profile design and be easy to fit between 2 shafts. And, of course, it should be CZPT to transmit power from 1 shaft to the other. These features are essential for high-speed applications.
How to Install a Roller Chain Coupling?
Ever-power chain couplings feature a unique single-pin design that greatly simplifies the installation process. Simply follow these simple steps.
- Install the oil seal on each hub
- Adjust the alignment of the shaft and coupling assembly
- Adjust the distance between the sprocket faces
- Thoroughly lubricate the coupling chain
- Install the chain to the coupling using the single pin coupling ring
- Firmly close and secure the coupling cover (optional, depending on operating conditions)
The chain coupling installation process is simpler and faster than conventional rigid couplings.
Additional information
Overview of Different Types of Pulleys
A pulley is a wheel mounted on a shaft or shaft. Its purpose is to facilitate the movement or change of direction of the cable or taut rope, and to transmit power between the cable and the shaft. Pulleys are typically used for lifting, winding or forklift applications. If you are building your own pulley system, the following design and installation considerations should be followed. This article will give you an overview of the different types of pulleys.
Pulley System Mechanics
There are many different ways to utilize the mechanism of the pulley system. The most basic pulley system consists of a fixed wheel and a support frame. Both components are connected by ropes or cables used to support the load. A pulley system is effective when the force required to lift the load is less than the weight of the object being lifted.
One way to use a pulley system is to suspend a block with a mass of 0.80 kg on a fixed pulley. Then another person can hang a bucket weighing up to 40kg. The weight of the bucket is transferred to the fixed pulley. The rope is attached to the pulley by a loop or sling. The rope will spin and pull on the barrel or block.
The pulley system is also an important tool for lifting heavy objects. Pulleys are often used in construction equipment to make lifting heavy objects easier. Gun tackles, yard tackles, and stationary tackle systems are common examples of these devices. They use the mechanical advantage of the design to guide the force that lifts the object. If you want to learn more about pulley systems, visit Vedantu. This website will provide you with a full description of the mechanism and its application.
Types of pulleys
Many different types of pulleys are used to lift heavy objects. They change the direction of the force and are an integral part of the cable system. Therefore, pulleys can move large and heavy objects more easily. However, before buying a pulley, you should have an idea of the benefits it brings. Below are some of the most common uses for pulleys.
Conical Pulley: Consists of several small conical pulleys connected to each other. The larger base of 1 pulley is used to guide the force. Round pulleys are used in the same way as step pulleys. They are widely used in industry and can be purchased at any hardware store. Pulleys are a huge investment, and the benefits they provide far outweigh the cost.
Movable Pulls: These are similar to their names, but work by allowing objects to move with the pull. Their movable parts are attached to the object to be lifted. They are also ideal for lifting heavy loads and can be found in utility elevators and construction cranes. They are also used in many other industries. They can also be made of wood, plastic or metal. The type of pulley you use depends on its intended use.
Mechanical Advantages of Pulley Systems
A pulley system is a simple machine that reduces the effort required to lift heavy loads. This mechanical advantage is proportional to the number of loops. For example, if you have a single rope loop, you must apply equal force to lift the weight. When you add another rope loop, you can lift heavier weights just by applying the same force. Therefore, a pulley system is an excellent way to use gravity to your advantage.
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the effectiveness of a pulley system. This ratio of force to work is called the mechanical advantage. In other words, if the rope system has a large mechanical advantage, it means that it requires less force to lift heavier loads. This advantage is usually measured in kilograms and is the same for all pulley systems. In general, the greater the mechanical advantage, the less effort is required to lift the load.
The mechanical advantage of a pulley system is that a single movable pulley requires half the force to lift an object than a single fixed pulley. Assuming frictionless bearings, the MA of a single pulley system is 2, similar to the MA of a single lever. A single pulley travels twice as much as it takes to move heavy objects manually.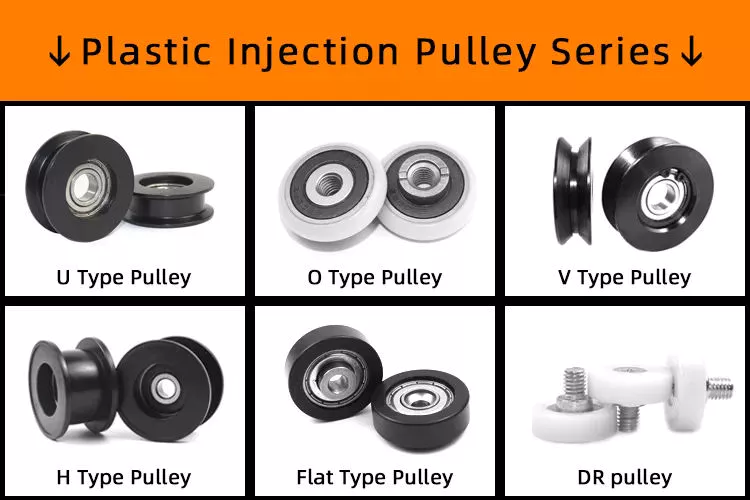
Considerations when designing and installing a pulley system
The capacity of the pulley depends on the type and diameter of the cable. Besides its diameter, its sheath should also support it well. The basic function of the pulley is also important. However, most people 10d to ignore the pulley selection process, resulting in ineffective load-pull capabilities. To avoid such problems, different parameters must be carefully considered during design and installation.
During the design and installation of the pulley system, the ratio of the cable diameter to the largest pulley diameter must be considered. Those who work in the industrial sector will have an idea of this ratio. The greater the D:d ratio, the greater the capacity of the cable to withstand the load. The best way to ensure secure design is to take the right information and use it to design a system that is both robust and secure.
When designing a pulley system, it is important to remember that the pulley needs to have enough power to operate safely. In addition to horsepower, the belt should have sufficient elongation to absorb shock loads. If the elongation of the belt is very small, it is very likely that the teeth will be sheared or broken, causing serious damage to the system. Extensive belt sag should be compensated for by offsetting the driven pulley. Finally, the frame supporting the pulley should be rigid. Otherwise, the non-rigid frame will cause center distance and tooth skipping changes.
Add more pulleys to the system
Adding more pulleys to the spool might have some effect. The friction between the rope and the pulley increases with the number of pulleys, which in practice limits the number of spools. The best solution is to combine the pulleys into 1 housing. If the load is small enough, adding a few pulleys probably won’t make a difference.
Using multiple pulleys allows a single load to be lifted with half the force required. The longer the rope, the greater the mechanical advantage. In fact, a spool can withstand a load of 100 N. Additionally, adding more pulleys quadrupled the mechanical advantage. In this case, a single 100 N load would require a force of 25 Newtons.
When the rope is used, it stretches as the weight of the object increases. This will make the rope longer, increasing its length and increasing the distance over which the load can be lifted. Eventually, the rope will break and the lifted object will fall. Then you will have to buy a new rope. It may seem like an expensive proposition, but it pays off in the long run.
cast iron pulley
Cast iron pulleys are the most popular choice among industrial users. They are made of solid cast iron and usually cost very little. Their rims are held in place by a mesh that extends from a central boss. They also have spokes and arms that hold them in place. These pulleys are ideal for a variety of applications including fan belts, compressors and conveyors.
V-groove drive pulleys are ideal for general purpose pulleys. It has an inner diameter of 1 inch and is commonly used in feeders and ventilation curtain systems. Its steel straps prevent rust and ensure it meets or exceeds industry standards. 3-1/2″ cast iron pulleys are also available. In addition to the V-groove drive pulley, there are similar pulleys for power transmission. The V-groove drive pulley is powder coated for added durability.
The cross section of the arm is elliptical, with the long axis twice as long as the short axis. The radius of the arm is equal to the diameter of the pulley. The thickness of the arm is a key factor to consider when purchasing a pulley. If you’re not sure which material you need, you can always consider wooden or steel pulleys. They are lighter and have a higher coefficient of friction than metal pulleys.
timing pulley
Plastic timing pulleys have many advantages over steel timing pulleys. On the 1 hand, they are lightweight and corrosion resistant, making them ideal for applications that do not require high torque and 10sile strength. Another benefit is their resistance to high temperatures. Plastic timing pulleys are ideal for applications involving flammable gases, solvents or particles. They can last for many years. For more information on the different types of plastic timing pulleys.
Vertical shaft drives require flanged timing pulleys. For large span drives, at least 1 of these pulleys must be flanged. The flange provides a secure connection to the shaft and prevents ratcheting of the timing belt. Finally, HTD timing belt teeth prevent timing belt ratcheting. These teeth need a large enough space to be seated. However, they can also cause a backlash. These pulleys are not suitable for applications where positional accuracy is critical.
Timing belt systems are designed to avoid such problems. The drive shaft and the driven shaft are aligned with each other. The pulleys are located on different planes and are connected by pitch lines. The pitch line of the timing pulley coincides with the pitch line of the belt. These pulleys are also easier to implement and maintain. It is better to use a synchronous system because the resulting gear system emits less noise than other systems.


